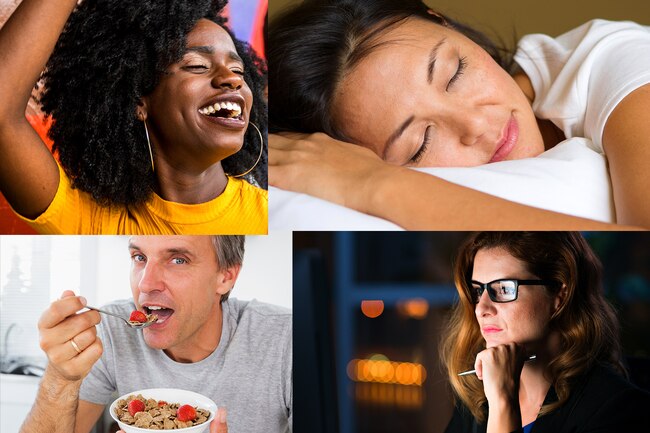
Flagging Energy
If your body is very low on B6, you can get anemia, which is too few red blood cells. That would make you feel tired and weak. Anemia can also come from not having enough iron in your body. Shortages of other vitamins, like B12 and folate, also may cause it.
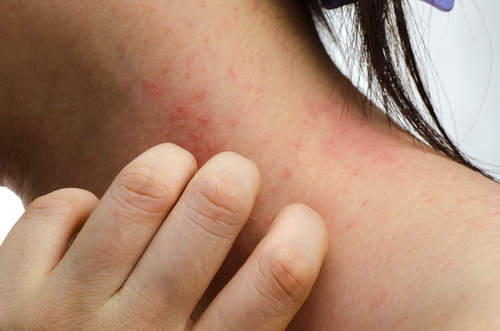
Rashes
Signs that you lack B6 can show up on your skin. Your body goes through chemical changes. That most often leads to a scaly, itchy rash, usually on your face, called seborrheic dermatitis. The rash may get more and more obvious with time. If you have a minor shortage, the symptoms could take months or years to show up.
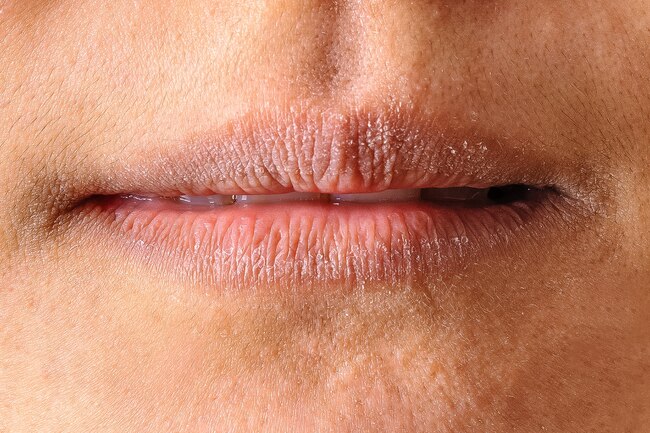
Dry, Cracked Lips
Your mouth could be a good place to spot any shortage of B6. Your lips might be scaly, and the corners could be cracked. Your tongue might swell.
Weak Immune System
A shortage of B6 may make it harder for your body to resist infections and diseases. That can turn into a vicious cycle. Cancer and other illnesses can deplete your B6 supply. So you’d need to get even more of the vitamin to make up for that. You can do that easily with a B6 supplement.
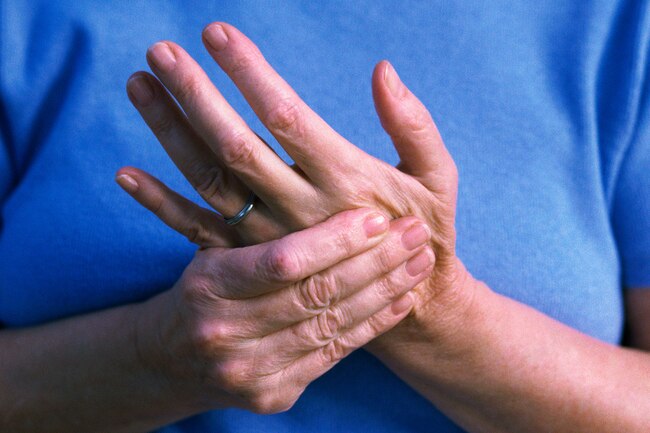
Numb Hands or Feet
Do your fingers tingle? Do your feet feel numb? The culprit may be a nerve disorder called peripheral neuropathy. Lack of B6 may help trigger it. It and other B vitamins like B12 are essential to keep your nerves healthy.
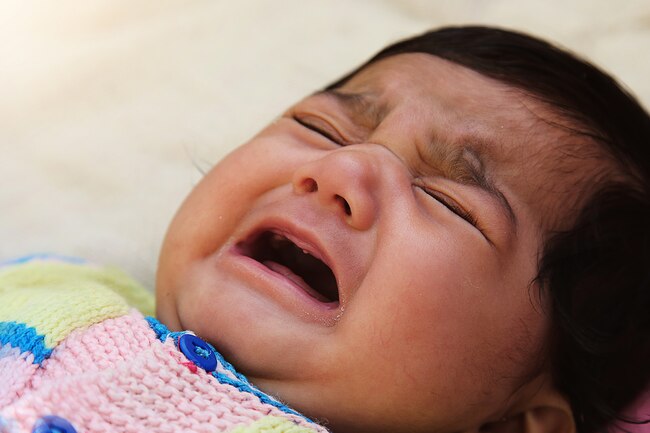
Cranky Baby
A fussy baby could be trying to tell you they’re low on B6. That could happen if you feed your infant nothing else but breast milk for more than about 6 months. Too little of the vitamin can even lead to seizures. It also can make your baby’s hearing extra sensitive so that noises can easily upset them.
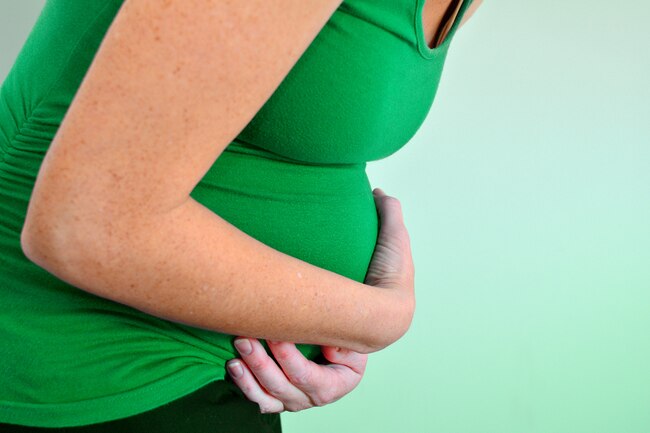
Morning Sickness
Moms-to-be need more B6 in their diet than anyone else. If you’re feeling sick with nausea or vomiting (and not just in the mornings), a B6 supplement may help. But you should take it only with your doctor’s guidance.
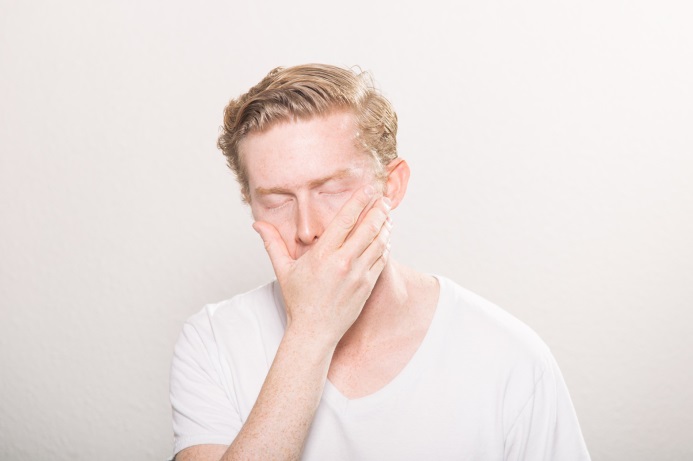
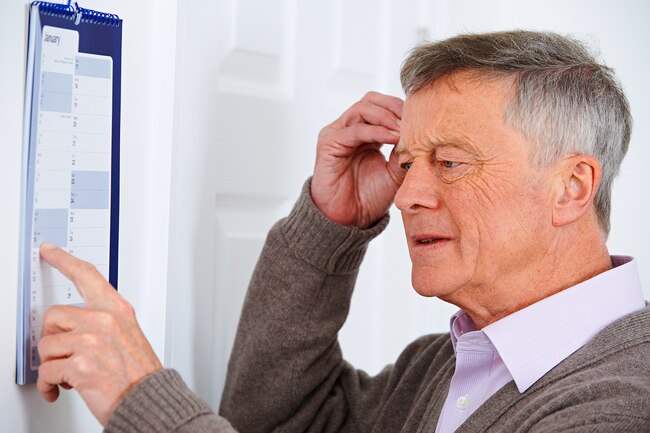
Foggy Brain
B6 helps regulate your mood and memory. If you notice feeling confused or sad, especially if you’re a senior, a shortage of this vitamin could be the reason. It may make you more likely to get depressed after a stroke, fractured hip, or other major illness. B6 sometimes works in tandem with other B vitamins. If you run low, it may slow your mental abilities.
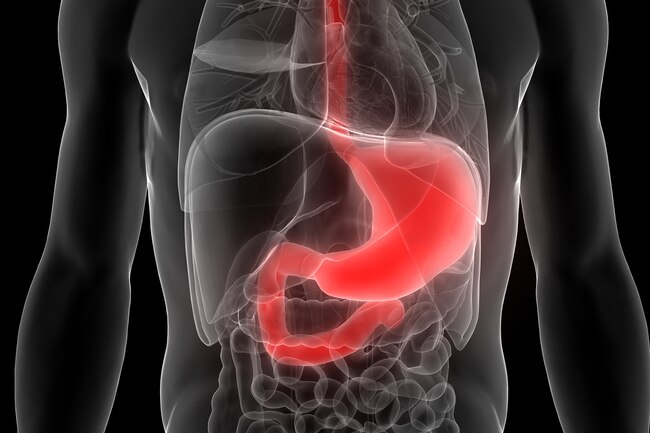
Cancer
Low B6 may play a role in your chances of having cancer. Researchers don’t know exactly why. But studies have linked a lack of B6 to stomach and esophageal cancers. A lack of the vitamin also may make you more likely to get cancers driven by steroid hormones, such as breast and prostate cancers.
Daily Dose
The amount of B6 you need each day depends mainly on your age. Babies 7-12 months old need 0.3 milligrams a day. You need more as you grow. If you’re over age 50, you need at least 5 times as much: 1.7 milligrams a day for men and 1.5 milligrams for women. Pregnant women need it most of all -- 1.9 milligrams a day.
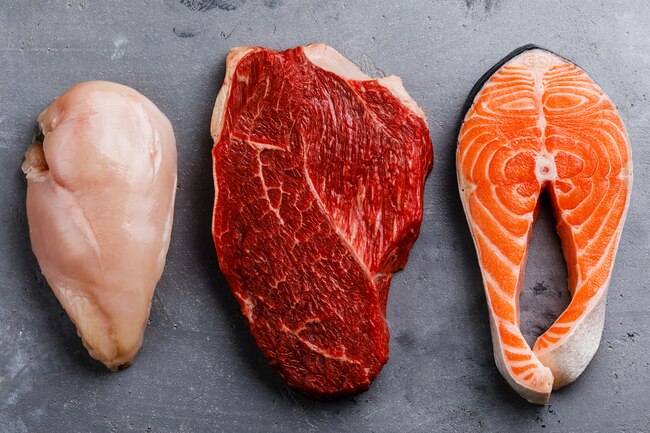
Source: Proteins
It’s easy to get all the B6 you need from foods. Poultry, beef, and fish are among the handiest sources. Just 3 ounces of tuna pack almost half of what an adult needs each day. The same amount of salmon will supply 30%, and chicken will give you 25%.
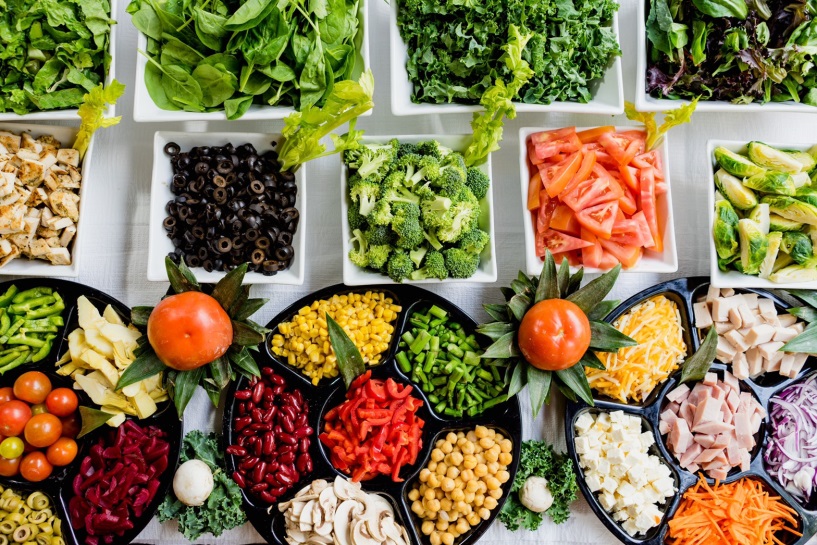
Sources: Veggies and Fruits
Love starchy vegetables like potatoes, yams, and corn? They’re some of the main ways that Americans get their B6. Fruits are another major source (except for citruses like oranges and grapefruits). One cup of chickpeas, aka garbanzo beans, will take care of half of your daily requirement
Causes of Shortage
Serious B6 deficiencies happen rarely. But some seniors may run low if they don’t eat enough food or because their bodies don’t absorb nutrients as well as before. Kidney disease and other conditions that keep your small intestine from taking in nutrients also can be culprits. So can alcohol abuse.
About Supplements?
If you’re unable to get enough B6 from foods, supplements can fill the gap. Most multivitamins have B6, or you can take it separately. Tell your doctor If you’re on any meds or taking other supplements. And go easy on it. Taking too much B6 might damage your nerves or give you sores, heartburn, or nausea. The safe daily limit for adults is less than 100 milligrams.

 Fish Oil Relieves Joint and Back Pain, Reducing Need for NSAIDs
Fish Oil Relieves Joint and Back Pain, Reducing Need for NSAIDs  Being Fit does not always mean Healthy
Being Fit does not always mean Healthy  7 Reasons Why Everyone Should Take Nutritional Supplements
7 Reasons Why Everyone Should Take Nutritional Supplements