|
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is an enzyme known chemically as a 1,4-benzoquinone. The “Q” in the name refers to the quinone chemical group, which are derived from aromatic compounds. The “10” refers to the 10 isoprenyl subunits in the tail of the CoQ10 molecule.
CoQ10 is a vitamin-like compound that’s found in most plant and animal cells, especially the mitochondria. It plays an essential role in generating adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is a requirement of aerobic respiration. Approximately 95 percent of the chemical energy generated by the human body comes from ATP, so the greatest concentration of CoQ10 is in organs such as the heart, kidney and liver that have the highest requirements for energy.
Animal protein is the richest dietary source of CoQ10, especially chicken livers and hearts. Dairy products also contain CoQ10, but at much lower levels than meat. The best vegetable sources of CoQ10 include parsley and perilla. Professor Fredrick L. Crane et al isolated CoQ10 in 1957, and its chemical structure was established by Dr. Karl Folkers et al in 1958.
The capability of manufacturing CoQ10 in commercial quantities and purity did not exist until the 1980s, when the number of studies on CoQ10 began to increase dramatically. These studies show that CoQ10 exhibits strong antioxidant activity, which allows it to support cellular health and function.
Uses of Coenzyme Q10
One of the most common uses of CoQ10 is support against the effects of aging. It is also used to support heart health, and maintain healthy cholesterol and support for the body’s natural ability to manage and regulate blood sugar levels.
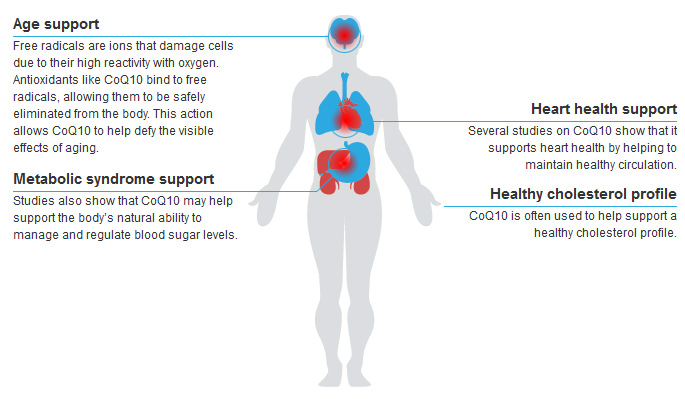
Signs You May Need Coenzyme Q10
The most common signs that you may have a CoQ10 deficiency are related to the cardiovascular system. Additional indications that you may need CoQ10 supplements include metabolic syndrome, poor gum health and poor digestive health. People who take statin drugs to lower cholesterol may also have low CoQ10 levels, since these drugs inhibit the biosynthesis of CoQ10. Additional signs of a CoQ10 deficiency include fatigue and muscle aches.
|

 Youre Not Getting Enough Vitamin B6
Youre Not Getting Enough Vitamin B6  Fish Oil Relieves Joint and Back Pain, Reducing Need for NSAIDs
Fish Oil Relieves Joint and Back Pain, Reducing Need for NSAIDs  Being Fit does not always mean Healthy
Being Fit does not always mean Healthy 
 Youre Not Getting Enough Vitamin B6
Youre Not Getting Enough Vitamin B6  Fish Oil Relieves Joint and Back Pain, Reducing Need for NSAIDs
Fish Oil Relieves Joint and Back Pain, Reducing Need for NSAIDs  Being Fit does not always mean Healthy
Being Fit does not always mean Healthy