Quercetin itself is not biologically available to humans, although some of its glycosides are. For example, an animal study showed that quercetin-4'-glucoside is converted to phenolic acids in the digestive tract. These acids aren’t produced by the digestion of quercetin, which implies that quercetin-4'-glucoside is more biologically active than quercetin. The same study showed that 96 percent of these phenolic acids were excreted within three days, indicating the low retention rate that’s characteristic of polyphenols.
The most significant biochemical role of quercetin in humans appears to be an increase in the secretion of insulin by beta cells in the pancreas. This action is the result of quercetin’s activation of L-type calcium channels in the beta cells. Quercetin also exhibits significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions.
Uses of Quercetin
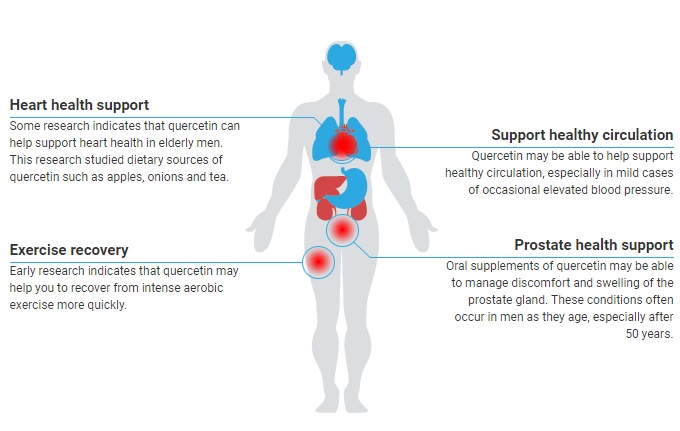
The long-term support of prostate health is one of the most common reasons for taking quercetin in health supplements. It is also used to support heart functions, including the circulatory system and exercise recovery.
Signs You May Need Quercetin
Swelling and discomfort of the prostate gland is one of the most significant signs that you may need quercetin supplements. Cardiovascular conditions such as an unhealthy cholesterol profile and poor circulation may indicate that quercetin may benefit you. Endurance athletes who want to improve their recovery after a workout may also need to use quercetin. Additional signs that may mean you could benefit from quercetin include chronic fatigue and seasonal conditions.
Other Ingredients That May Be Of Interest
Hesperidin - Hesperidin is a flavanone that is primarily found in citrus fruits and plays an important role in plant defense. It is most often used to maintain circulation in the legs.
Resveratrol - Resveratrol is a phenol found in several plants, especially grapes. The most common uses of resveratrol include the management of the circulatory system and maintenance of a healthy cholesterol profile.

 Total Women's Health
Total Women's Health  Total Balance - New Immunity Blend
Total Balance - New Immunity Blend  The Science of Digestion
The Science of Digestion 
 Total Women's Health
Total Women's Health  Total Balance - New Immunity Blend
Total Balance - New Immunity Blend  The Science of Digestion
The Science of Digestion